|
|
|
|
|
Giant Fibroepithelial Polyp of Vulva – A Rarest of its Occurrence
|
|
|
potency of naloxone and naltrexone narcan vs naltrexone
From the Department of Surgery, Bhakti Vedanta Hospital, Srishti Complex, Mira Road East, Thane, Maharashtra-401017, India. |
|
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Author:
|
Dr. BC Shah
Email: vaishnavasevadasa@gmail.com
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Received:
07-JUN-2014 |
Accepted:
24-JUN-2014 |
Published Online:
20-JUL-2014 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Abstract
|
|
|
|
Fibro epithelial stromal polyps which are benign mesenchymal lesions that typically occur in skin, oral cavity, urinary tract and genital area pose diagnostic problems because of bizarre cytomorphology. Genital presentation has a greater predilection for the vulvovaginal region and rarely the cervix. Cases of fibro epithelial polyp in vulva have been rarely reported and usually they do not grow larger than 5 cm in diameter and are found incidentally during routine gynecologic exams. Diagnosis mainly based on histopathology has to be done to rule out malignancy and also to differentiate from other lesions like angiomyxoma which mimics fibro epithelial polyps. The case report presented is a rarest of its kind as regards to its size because the polyp in this patient measured 35x23x11 cm and weighing 10 kg which becomes the largest polyp reported ever. |
|
|
|
|
|
Keywords :
|
Vulval Neoplasms, Polyps, Cervix Uteri, Myxoma, Pregnancy, Hormone Replacement Therapy.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6go6ckt5b8|3000F7576AC3|Tab_Articles|Fulltext|0xf1ff88e8050000000b03000001000800 6go6ckt5b5idvals|343 6go6ckt5b5|2000F757Tab_Articles|Fulltext Introduction
Fibro epithelial stromal polyps are a type of benign mesenchymal hormone sensitive lesions most commonly seen in pregnant women. Skin, oral cavity, urinary tract, breast and genital area are common areas of presentation of which genital presentation is much more common and has a greater predilection for vulvovaginal region and rarely the cervix [1]. However, they can also be seen in premenopausal females who are on hormone replacement therapy. They always pose diagnostic problems because of their resemblance to various other mesenchymal lesions. Cases of fibro epithelial polyp in vulva have been reported and usually they do not grow larger than 5 cm in diameter. Because of their smaller size they are usually identified on routine gynecological examination only. However, the largest size reported ever was 28x27x12 cm in a 16 year old women [2]. The case report presented is a rarest of its kind as regards to its size and weight because the polyp in this patient measured 35x23x11 cm and weighing 10 kg which becomes the largest polyp reported ever.
Case Report
A 56 year old female reported to our hospital with the complaint of difficulty during walking because of a growing mass between her thighs. History revealed that the mass initially started as a small growth 40 years back and it had been growing since then. The growth grew rapidly in size for the past six years. No significant medical or surgical history was present. The patient had not taken consultation since so many years because of personal reasons being the site of its presentation. She attained menopause six years back and no significant gynecological history was present. She was a non-smoker and denied alcohol or drug use. Physical examination revealed a large, non-tender, skin colored, pumpkin sized broad based pedunculated mass extending from the right labium majus [Fig.1]. Transvaginal ultrasound showed atrophic uterus and ovaries but also described a broad-based encapsulated soft tissue mass from the right labium at the level of the clitoris. Surgery being the only treatment option, surgical removal of the mass was planned after obtaining consent from the patient and explaining the procedure in detail. The tumor arising from labia majora was excised completely [Fig.2] and primary closure of wound was carried out. Consent of the patient was obtained for publishing this as a case report.
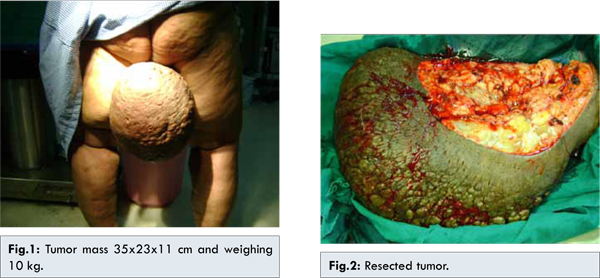
In the present case report, a mass in a 56 year old female has been described. The mass was diagnosed to be a giant fibro epithelial stromal polyp which is the largest ever reported measuring 35x23x11 cm and weighing 10 kg. The fibro epithelial stromal polyp, also called “cellular pseudoangiomatous fibroepithelial stromal polyps” was described originally by Norris and Taylor in 1966 like a benign injury [3]. These polypoid exophytic tumor growth arises from proliferation of mesenchymal cells within the hormone sensitive sub epithelial stromal layer of the lower genital tract in females of reproductive age [4,5]. Symptoms include bleeding, discharge and discomfort. Usually the margins are unidentifiable as they merge with the normal tissue. Histologically, they contain conspicuous fibrovascular core and a hypocellular stroma. However, this bizarre stromal cytomorphology, atypical mitosis and hypercellularity often lead to misdiagnosis [6]. Malignancy must be excluded in every diagnosis of fibro epithelial stromal polyp. Various other lesions like leiomyomas, superficial angiomyxoma, perineureomas and neurofibromas mimic fibro epithelial polyps [7]. For this reason final diagnosis is always based on microscopic findings. Microscopically, the most characteristic feature of a fibro epithelial stromal polyp is the presence of stellate and multinucleate stromal cells identified near the epithelial-stromal interface [8]. Microscopic evaluation of the lesion in this case revealed loose fibrocollagenous and fibrofatty tissue lined by unremarkable stratified squamous epithelium. The stroma was traversed by small blood vessels and chronic inflammatory cells. Cases of reoccurrence of fibro epithelial polyps raise concern about complete surgical excision [9]. As a result, all patients with this diagnosis should be followed up on long term and managed appropriately after initial treatment.
Conclusion
Fibro epithelial stromal polyps are benign, mesenchymal lesions that typically occur in women of child-bearing age. These polyps have a predilection for the vulval region and although they typically are small in size; they sometimes can grow as large as 10 kilograms and 35 cm in diameter as seen in our presenting case. Although benign, the polyp mimics some more serious and malignant growths in appearance and as a result, microscopic evaluation of the polyp is critical in the exclusion of malignancy.
References
- Ostor AG, Fortune DW, Riley CB. Fibroepithelial polyps with atypical stromal cells (pseudosarcoma botryoides) of vulva and vagina. A report of 13 cases. Int J Gynecol Pathol 1988;7:351-360.
- Oh MJ, Kee MJ, Kang WD, Kim SM, Choi HS. A case of giant fibroepithelial polyp of vulva. Korean J Obstet Gynecol 2010;53:194-197.
- Norris HJ, Taylor HB. Polyps of the vagina. The benign injury resembling sarcoma botryoides. Cancer 1966;19:227-232.
- Halvorsen TB, Johannesen E. Fibroepithelial polyps of the vagina: plows they old granulation tissue polyps? J Clin Pathol 1992;45:235-240.
- Wani Y, Fujioka Y. A vulvar fibroepithelial stromal polyp appearing in infancy. Japan Am J Dermatopathol 2009;31:465-467.
- Nucci MR, Young RH, Fletcher CD. Cellular pseudosarcomatous fibroepithelial stromal polyps of the lower female genital tract: an under recognized lesion often misdiagnosed as sarcoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2000;24:231-240.
- Shaaban AM, Turton EPL, Merchant W. An unusual case of a large fibroepithelial stromal polyp presenting as a nipple mass. BMC Research Notes 2013;6:345.
- Nucci MR, Olivia E. Gynecologic Pathology: A Volume in Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series. Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone; 2009:31-32.
- Han X, Shen T, Rojas-Espaillat LA, Hernandez E. Giant cell fibroblastoma of the vulva at the site of a previous fibroepithelial stromal polyp: a case report. J Low Genit Tract Dis 2007;11:112-117.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Search Google Scholar for
|
|
|
Article Statistics |
|
Shah BC, Degloorkar S, Rao AGiant Fibroepithelial Polyp of Vulva – A Rarest of its Occurrence.JCR 2014;4:263-265 |
|
Shah BC, Degloorkar S, Rao AGiant Fibroepithelial Polyp of Vulva – A Rarest of its Occurrence.JCR [serial online] 2014[cited 2025 Oct 26];4:263-265. Available from: http://www.casereports.in/articles/4/2/Giant-Fibroepithelial-Polyp-of-Vulva.html |

|
|
|
|
|